티스토리 뷰
Chaining Hash Table
/*Chaining HashTable*/
class ChainingHashTable {
public static final int TABLE_SIZE = 10;
private HashItems[] hashTable;
//생성자
public ChainingHashTable() {
this.hashTable = new HashItems[TABLE_SIZE];
}
//hash code
int getHashCode(String key) {
int hashCode = 0;
for (char c : key.toCharArray())
hashCode += c;
return hashCode;
}
//hash code를 index
private int convertToIndex(int key) {
return key % TABLE_SIZE;
}
//삽입
public void put(String key, String value) {
int hashCode = getHashCode(key);
int hashArrayIndex = convertToIndex(hashCode);
if (hashTable[hashArrayIndex] == null) {
//hash table의 슬롯이 비어 있으면 바로 삽입
System.out.println("no collision simple insertion");
hashTable[hashArrayIndex] = new HashItems(key, value);
} else {
//hash table의 슬롯이 비어있지 않으면
System.out.println("collision when inserting with key : " + key);
HashItems hashItem = hashTable[hashArrayIndex]; //hash table 슬롯에 저장된 첫번째 데이터를 가져온다.
//연결리스트 마지막까지 탐색을 수행한다.
while (hashItem.getNextHashItem() != null) {
hashItem = hashItem.getNextHashItem();
System.out.println("considering the next item in linked list" + hashItem.getValue());
}
//마지막으로 연결 리스트 다음에 삽입
System.out.println("finally we have found the place to insert...");
hashItem.setNextHashItem(new HashItems(key, value));
}
}
//반환
public String get(String key) {
int hashCode = getHashCode(key);
int hashArrayIndex = convertToIndex(hashCode);
if (hashTable[hashArrayIndex] == null)
return "not found";
HashItems hashItem = hashTable[hashArrayIndex];
while (hashItem != null && hashItem.getKey() != key)
hashItem = hashItem.getNextHashItem();
if (hashItem == null)
return "not found";
else
return hashItem.getValue();
}
class HashItems {
private String key;
private String value;
private HashItems nextHashItem;
public HashItems(String key, String value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public HashItems getNextHashItem() {
return nextHashItem;
}
public void setNextHashItem(HashItems nextHashItem) {
this.nextHashItem = nextHashItem;
}
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
}Linear Probing HashTable
/*Linear Probing HashTable*/
class LinearProbingHashTable {
public static final int TABLE_SIZE = 10;
private HashItems[] hashTable;
public LinearProbingHashTable() {
this.hashTable = new HashItems[TABLE_SIZE];
}
private int convertToIndex(int hashcode) {
return hashcode % TABLE_SIZE;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
//충돌을 발생하기 위해서 key값을 hashcode로 바로 사용
//key값이 1, 11, 21 ..이 들어오면 충돌 발생
int hashArrayIndex = convertToIndex(key);
System.out.println("put() method called with value : " + value + ", hashArrayIndex : " + hashArrayIndex);
//충돌이 없을 때까지 반복 수행
while (hashTable[hashArrayIndex] != null) {
//인덱스 1 씩 증가
hashArrayIndex = (hashArrayIndex + 1) % TABLE_SIZE;
System.out.println("collision -> move to next index : " + hashArrayIndex);
}
System.out.println("Inserted finally with index : " + hashArrayIndex);
hashTable[hashArrayIndex] = new HashItems(key, value);
}
public int get(int key) {
int hashArrayIndex = convertToIndex(key);
while (hashTable[hashArrayIndex] != null && hashTable[hashArrayIndex].getKey() != key) {
hashArrayIndex = (hashArrayIndex + 1) % TABLE_SIZE;
System.out.println("not matched, move to next index : " + hashArrayIndex);
}
if (hashTable[hashArrayIndex] == null) return -1;
else return hashTable[hashArrayIndex].getValue();
}
class HashItems {
private int key;
private int value;
public int getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public HashItems getNextHashItem() {
return nextHashItem;
}
public void setNextHashItem(HashItems nextHashItem) {
this.nextHashItem = nextHashItem;
}
private HashItems nextHashItem;
public HashItems(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
}
Test Main
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
chaining hash table test : key,value type은 string
*/
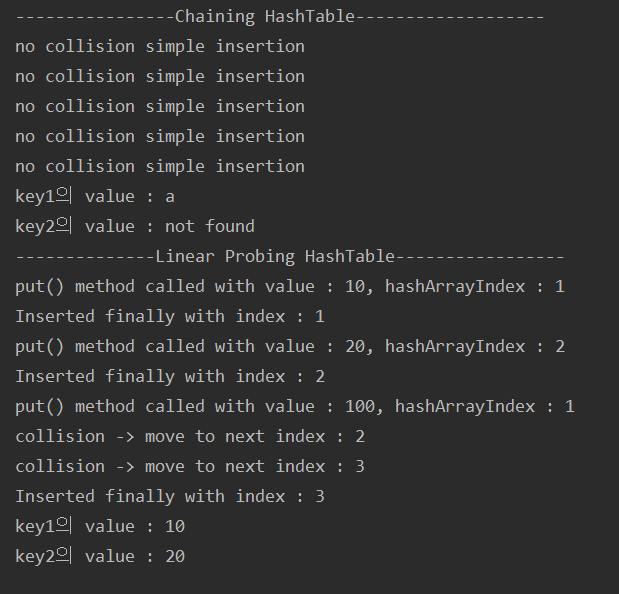
System.out.println("----------------Chaining HashTable-------------------");
ChainingHashTable ht = new ChainingHashTable();
ht.put("key1", "a");
ht.put("key2", "ab");
ht.put("key3", "abc");
ht.put("key4", "abcd");
ht.put("key5", "abcde");
System.out.println("key1의 value : " + ht.get("key1"));
System.out.println("key2의 value : " + ht.get("key6"));
System.out.println("--------------Linear Probing HashTable-----------------");
LinearProbingHashTable ht2 = new LinearProbingHashTable();
ht2.put(1,10);
ht2.put(2,20);
ht2.put(11,100); //충돌 발생
System.out.println("key1의 value : " + ht2.get(1));
System.out.println("key2의 value : " + ht2.get(2));
}결과
참고 및 출처
'자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Stack(스택) & Queue(큐) (0) | 2020.08.06 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 힙(Heep) & 우선순위 큐 (0) | 2020.02.24 |
| [자료구조] LRU Cache 알고리즘 (0) | 2020.01.02 |
| [자료구조] Array VS LinkedList (0) | 2019.12.17 |
| 메모리 저장 구조 - 변수사용에 따른 메모리 효율 (0) | 2019.12.03 |
댓글
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- hash
- 기능개발
- SRTN
- MLQ
- MFQ
- 우선순위큐
- Process Scheduling
- algorithm
- DFS
- 프로그래머스
- binarySearch
- 백트래킹
- Android
- hashtable
- 4-way-handshake
- 알고리즘
- 사회망서비스
- 프로세스 스케줄링
- loss function
- 농협정보시스템IT
- Objective function
- git
- programmers
- java
- N-Queen
- 네트워크
- 3-way-handshake
- 자료구조
- 백 트래킹
- SWExpert
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
글 보관함
